Microfollicular Adenoma of the Thyroid
Endocrine system
Microfollicular Adenoma of the Thyroid
A microfollicular adenoma of the thyroid is a benign (non-cancerous) thyroid nodule characterized by small, tightly packed follicles. It is typically identified through a thyroid biopsy or surgery.
Key Features
• Histology: Small follicles lined by a single layer of follicular cells with scant colloid.
• Benign Nature: Despite being non-cancerous, it can resemble follicular carcinoma on fine-needle aspiration (FNA), requiring further evaluation.
• Differential Diagnosis: Difficult to distinguish from follicular carcinoma cytologically, as both may exhibit a microfollicular pattern.
Diagnosis
• Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA): Typically reveals a follicular lesion but cannot differentiate between benign and malignant forms.
• Surgical Excision and Histopathology: Required for definitive diagnosis. The presence of capsular or vascular invasion indicates follicular carcinoma rather than an adenoma.
Management
• Observation: Appropriate for cases with benign cytological features, with regular monitoring.
• Surgery: Recommended if there is suspicion of malignancy (e.g., indeterminate cytology or concerning features), with options including lobectomy or thyroidectomy.
Gross Appearance of Microfollicular Adenoma
1. Size and Shape:
o Well-circumscribed, solitary nodule.
o Typically ranges from 1 to 3 cm in diameter.
2. Capsule:
o Encapsulated with a thin, fibrous capsule, aiding in distinguishing it from follicular carcinoma.
3. Color and Texture:
o Tan to brown or grayish cut surface.
o Homogeneous appearance, usually solid, firm, and rubbery.
4. Cystic Changes:
o May have small cystic spaces or colloid-filled follicles; significant cystic degeneration is rare.
5. Hemorrhage and Calcifications:
o Foci of hemorrhage, fibrosis, or calcification may be present but are not prominent.
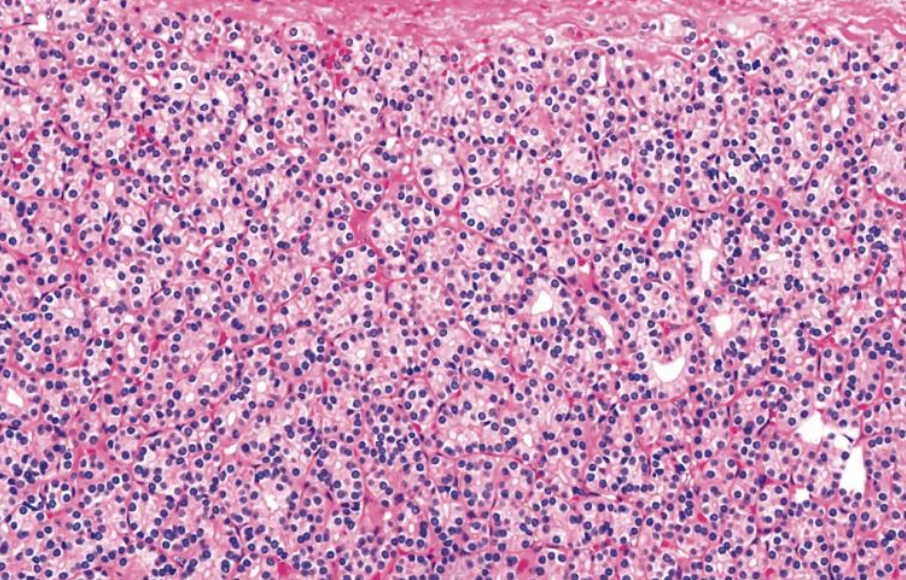
Microscopic Appearance of Microfollicular Adenoma
1. Follicular Architecture:
o Composed of small, tightly packed follicles (microfollicles) with little or no colloid.
2. Follicular Cells:
o Lined by cuboidal to low columnar cells with uniform, bland nuclei.
o Cells may have eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm.
3. Capsule:
o Surrounded by a well-defined, fibrous capsule.
o No capsular or vascular invasion (a critical feature distinguishing it from follicular carcinoma).
4. Stromal Features:
o Minimal stromal involvement, with possible areas of fibrosis.
5. Nuclear Features:
o Round to oval nuclei, lacking features of papillary thyroid carcinoma (e.g., nuclear grooves or pseudoinclusions).
6. Colloid:
o Scant or absent, contributing to the microfollicular pattern.
7. Mitotic Activity:
o Low, supporting its benign nature.
8. Other Patterns:
o Mixed microfollicular and normofollicular areas or occasional trabecular/solid patterns, but without malignant features.